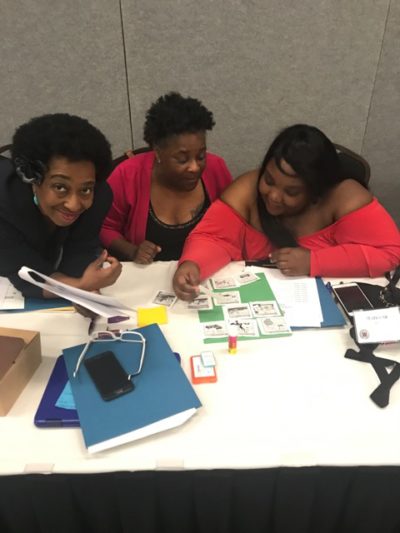
Yes, you can be an advocate! Here’s how.
Download the slides here.
And here’s more specific information about how state laws get made–and changed–from our 2020-2021 State Legislative Advocacy webinar series:
Advocacy Glossary
*Sourced partly from Bolder Advocacy, the Women’s Foundation of California, & USA.govA
Administrative Advocacy
Efforts to influence actions of the Executive Branch, including commenting on regulations, Executive Orders, and other policies
Administrative Agencies
Administrative agencies are lawmaking bodies with limited powers given by Congress. Agencies specialize in specific issues that require expertise. Most administrative agencies fall under the supervision of the President, examples include The Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) and The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI). There are also independent administrative agencies like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). States also have their own administrative agencies
Advocacy
Advocacy is any action that speaks in favor of, recommends, argues for a cause, supports or defends, or pleads on behalf of others. It includes public education, regulatory work, litigation, and work before administrative bodies, lobbying, voter registration, voter education, and more
Amendment
Additions or changes to bills that are proposed after the bill has been introduced
Appropriations
Money set aside for specific federal government departments, agencies, and programs. The money provides funding for operations, staff, equipment, and activities
B
Ballot Initiatives
Petition signed by a certain minimum number of registered voters to bring a public vote on a proposed law or constitutional amendment
Ballot Measure
Ballot measures allow voters to propose and enact laws directly. They include ballot initiatives, constitutional amendments, bond measures, and referenda
Bird-dogging
When used in a political context, the term refers to activists who seek out the candidates, pin them down with specific questions or information, and get their views on the record
Bond Measure
When a state government, or a local unit of government (city, county, school district), places a question before the voters as a ballot measure that asks them to approve or deny additional proposed spending
C
Cabinet
A group of advisers to the president, made up of the heads of the executive departments of the government
Call to Action
A specific means of encouraging someone to take lobbying action. A call to action must include at least one of the following actions: 1) telling someone to contact a legislator; 2) providing information on how someone can contact their legislator, such as providing the phone number or address; 3) providing a way for someone to contact their legislator, such as a postcard, petition, or email form; or 4) identifying a legislator who will vote on the legislation as being for, against, or undecided about the legislation
Candidate Debate
A public debate where candidates for a public office directly engage each other at the same time on particular topics
Candidate Forum
A public meeting or assembly allowing for open discussion of issues by candidates where candidates appear one at a time
Checks and Balances
In the U.S.- refers to the specific powers that each branch of government (legislative, executive, judicial) has that allows them to challenge the other branches. Creates a system where each branch is accountable to the other two
Committee Chair
Current presiding (in-charge) officer of a committee
Conference Committee
A temporary committee made up of both House and Senate members, which is formed resolve differences between versions of the same legislation that has passed both chambers
Confirmation (Senate)
The president is allowed to choose people to fill certain government positions, but for some positions the Senate must approve the president’s nomination first, approval is known as confirmation. The confirmation process usually involves hearings, where Senators get a chance to ask the nominee questions
Congressional Caucus
Group of members of the United States Congress that meets to advance common legislative goals. Formally, caucuses are formed as congressional member organizations through the House of Representatives and governed under the rules of that chamber
Congressional Committees
Legislative sub-organization in Congress that handles a specific duty. Committee members develop specialized knowledge of the matters under their jurisdiction
Community Organizing
Educating and mobilizing individuals to influence public policy
Constituent
A voter represented by an elected official in government
Continuing Resolution
Temporary funding bills passed to keep the government operating while regular appropriations bills are still in the process of being passed
D
Direct Lobbying
Occurs when an organization communicates with a legislator or legislative staff member about a specific piece of legislation and reflects a view on that legislation. Direct Lobbying also includes any communication with the general public expressing a view about a ballot initiative, referendum, bond measure, or similar procedure
E
Electoral-Related Activity
Electoral-related activities includes “partisan election-related activity” (activity that supports or opposes candidates for public office) and “nonpartisan election-related activity” (activities that do not attempt to influence an election by supporting or opposing a candidate).
Electorate
All the people in a country or area who are entitled to vote in an election
Entitlement Programs
Includes Medicaid, Medicare, Social Security, Unemployment and Welfare Programs. Entitlement programs are rights granted to citizens and certain non-citizens by federal law
Executive Branch
The executive branch is one of the three branches of the U.S. government, it carries out and enforces laws. It includes the president, vice president, the cabinet, executive departments, independent agencies, and other boards, commissions, and committees
Executive Order
An order issued by the president, governor, or mayor that is not legislation but has the force and effect of law. They can be overturned by a new administration and usually require further action by agencies in order to have an effect
F
Federal Budget
Plan for the annual public expenses of the United States
Federal Register
Daily publication of the U.S. federal government that issues proposed and final administrative rules of federal agencies
Federalism
Refers to a system of government where powers are divided between one central authority (example: the U.S. federal government) and multiple constituent authorities (example: U.S. state and local governments)
Filibuster
Political tactic where one or more members of congress debate over a proposed piece of legislation for a prolonged period of time in order to delay or entirely prevent a decision being made on the proposal
Floor
Used to reference the House or Senate chamber where bills are discussed and voted upon
G
General Election
A regular election of candidates for office
Grassroots Lobbying
A communication with the general public that reflects a view on specific legislation and includes a call to action that encourages people to contact their legislative representatives or staff in order influence support or opposition to that legislation
H
Hearing
A committee meeting called to gather information on a subject or considering specific legislation
House of Representatives
The House is the lower chamber of the U.S. Congress, it is comprised of Representatives who represent a particular district in their state. The number of total district seats in each state is based on population size, determined by the U.S. Census. The total number of Representatives is capped at 435. Responsibilities of the House include passing laws known as bills, which, after being agreed to by the Senate, are sent to the president for consideration. The House also has the the power to start all bills related to revenue (collecting money) and impeach federal officers. The presiding officer is the Speaker of the House, who is elected by the members and so is usually the leader of the majority party
I
Issue Advocacy
An organization communicating positions on issues of social concern that are related to the organization’s mission. Advocacy might include education or attempting to influence the public on subjects such as health care, gun safety, worker rights or environmental protection. The term is commonly used to mean all policy-related activities that are not intended to influence election of a candidate for office.
J
Judicial Branch
The judicial branch or court system represents one of the three branches of the U.S. government, they decide arguments about the meaning of laws and how they are applied. They also decide if laws violate the Constitution—this is known as judicial review, and it is how federal courts provide checks and balances on the legislative and executive branches
L
Legislation
Also known as bills, includes actions by Congress, a state legislature, a similar local legislative body, or any actions by the general public in a referendum question, initiative petition, or proposed constitutional amendment.
Legislative Advocacy
Efforts to change policy through the legislative branch of government (state or federal). This may include lobbying or other communications with the legislative branch
Legislative Branch
The legislative or lawmaking branch of government is one of the three branches of the U.S. government. It has a two-house (“bicameral”) Congress—the Senate and the House of Representatives—and agencies that support Congress
Legislative Scorecard
Tallies of the votes cast by sitting legislators on bills. These are sometimes referred to as voting records
Line Item Veto
The power of a governor, or other elected executive to reject individual sections of a bill and pass the rest of it without sending it back to the legislature. The U.S. president no longer has this power after the Supreme Court ruled it was unconstitutional for the president to make law, a power that belongs to Congress
Litigation
A lawsuit or any dispute brought to court to enforce a particular right
Lobbying
In general, lobbying is an attempt to influence specific legislation by communicating views to legislators or asking people to contact their legislators. See also direct lobbying and grassroots lobbying
M
Majority Party
Refers to the political party that has the most seats in the House or Senate
Majority Vote
A vote of more than half of the legislative body considering a measure. 51 in the U.S. Senate, and 218 in the House
Mandatory Spending
Also known as direct spending, refers to spending enacted by law, but not dependent on an bill. Most mandatory spending consists of entitlement programs such as Social Security benefits, Medicare, and Medicaid
Motion
A formal call for an action made by a legislator during a committee hearing or Floor session
N
Needs Assessment
Process for determining and addressing needs, or “gaps” between what exists and what is wanted or needed. The “gap” between the two must be measured to figure out the need
O
Omnibus Bill
Proposed law that covers a number of diverse or unrelated topics
P
Phone Banking
Involves volunteers calling through lists of voters and talking to them about a candidate for office, legislation, or a policy issue. Phone banking can be used to provide information, sway voters, get out the vote (GOTV), recruit volunteers, and raise funds.
Pocket Veto
An indirect veto of a legislative bill by the president or a governor by keeping the bill unsigned until it is too late for it to be dealt with during the legislative session
Policy Brief
Summary of a particular issue, the policy options to deal with it, and some recommendations on the best option. Usually aimed at government decision makers/legislators and others who are interested in making or changing policy
Primary Election
An opening election to appoint delegates to a party conference or to select the candidates for a general, especially presidential, election. Some states have closed primaries, where only voters who are registered to a particular party can vote for candidates from that party. States that do not require party registration have open primaries
Public Commenting
Process that allows individuals, organizations, agencies, and businesses to provide written input on government decisions, usually executive orders or proposed rules drafted by agencies
R
Ratify (Treaties)
The president negotiate treaties, but the treaty must be consented to by a two-thirds vote in the Senate. Only after the Senate approves a treaty can the president ratify it. When the president ratifies a treaty, it means they sign or give formal consent to it and make it officially valid. Once it is ratified, it becomes binding on all the states. Congress sometimes must pass additional legislation to give a treaty full effect
Recall Vote
A special election on the question of whether an elected official should be removed from office
Referendum
Direct vote in which an entire voter base is invited to vote on a particular proposal
Regular Session
A session (of Congress) that happens at regular intervals or specified times
Regulation
A rule or order that has the force of law that originates from the Executive Branch (usually from an agency) and deals with the specifics of a program
Rules/Rulemaking (Administrative Agencies)
Process that executive and independent agencies use to create, or “promulgate” regulations. In general, legislatures pass statutes, then agencies create more detailed regulations through rulemaking to help that statute take effect
S
Senate
The upper chamber of the U.S. Congress. Made up of two elected Senators from each state for a total of 100 Senators. Responsibilities of the Senate include passing laws known as bills, which, after being agreed to by the House, are sent to the president for consideration. The Senate also has the power to ratify treaties, confirm cabinet secretaries, Supreme Court justices, federal judges, and ambassadors among others, and conduct trials of those impeached by the House. The presiding officer of the Senate is the vice president of the United States, who is president of the Senate. In the vice president’s absence, the President Pro Tempore, usually the senior member of the party holding a majority of seats, presides.
Separation of Powers
The division of government power between different branches with different roles, to avoid any one branch from having too much power and to create checks and balances
Session
The period during which the legislature meets. The legislature may meet in either regular or special session.
Special Session
A special session (or extraordinary session) is a period when the Congress meets outside of the normal legislative session.
Sponsor
The member of the legislature, private individual, or group who creates a measure and advocates passing it.
Supreme Court
The highest federal court, made up of nine justices (including one Chief Justice) and superior to all other courts in the nation. Justices serve until they retire or pass away.
V
Veto
Power, used by presidents and governors, to stop an official action, usually the passage of legislation. Legislation can be passed over a veto if it is overridden. Overriding of a veto does not happen often and requires a two-thirds vote in each Chamber of the U.S. Congress. State legislatures have a similar ability to override vetoes.
Voter Guide
Printed or electronic material that compares the candidates in a race, usually based on their positions on issues. The information in voter guides is often gathered through a questionnaire sent to the candidates in a race, as well as from public sources such as campaign websites and legislative records.
W
White Paper
Persuasive, in-depth report provided by an expert on a specific topic that presents a problem and provides a solution
Get a handle on the basic structure of the government
It’s important to know which level of government is responsible for what to make sure that we know who we need to target our advocacy efforts on. For example, it’s pretty much useless to ask our Congressperson or U.S. Senator to expand Medicaid in our state: That’s a decision made by state government. Same for HIV criminalization laws: These are state-by-state, and if we want to change the laws in our state, the most important lawmakers to address the issue with are state legislators. Our members of Congress won’t be able to help us, and talking to them about it is not a great use of their time or ours.
In the recorded webinar below, presenters discuss the differences and similarities between state and federal advocacy, and which laws and policies are decided at which level. You can download the slides here. And find information about your state’s legislative session dates here.
Hone your policy analysis skills to tackle the issues that matter most to you
This webinar from the PWN Policy Fellowship is an introduction into what policy research is and how to use effective research strategies to do it well.